Image Source: Google
As the world continues to grapple with the impacts of climate change, there is growing interest in innovative solutions that can help mitigate the effects of rising greenhouse gas emissions. One such solution that has garnered significant attention in recent years is Direct Air Capture (DAC). DAC is a technology that involves capturing carbon dioxide directly from the air and storing it in a secure location to prevent it from contributing to the greenhouse effect. This process is seen as a promising tool in the fight against climate change, as it offers a way to remove CO2 from the atmosphere and reduce the overall levels of greenhouse gases.
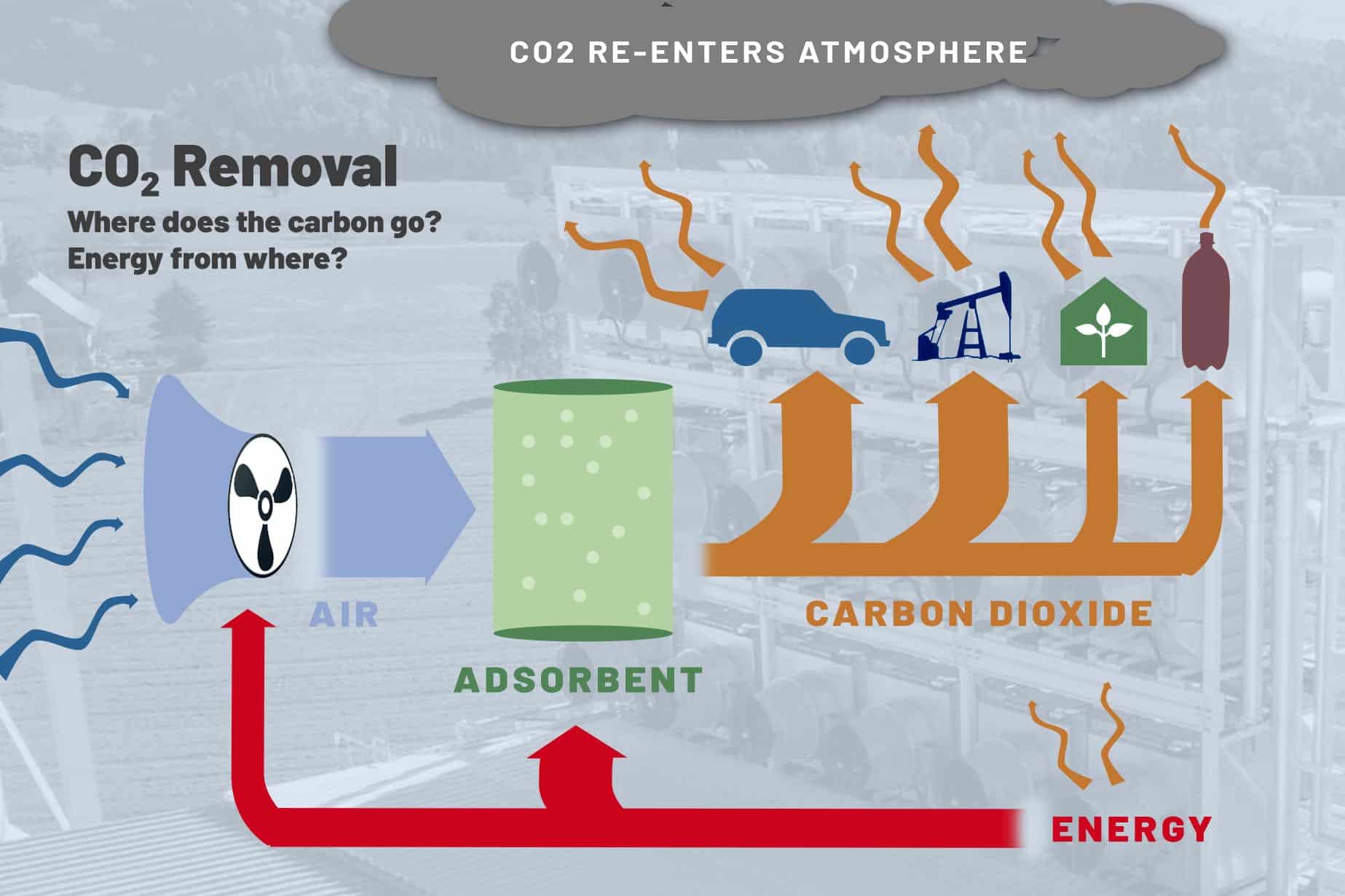
So, how does Direct Air Capture work? The process involves several key steps that allow for the efficient capture and storage of carbon dioxide. First, air containing CO2 is brought into contact with a sorbent material, which selectively binds to the carbon dioxide molecules. This sorbent material is then separated from the air, allowing the captured CO2 to be extracted and stored. The captured carbon dioxide can then be either stored underground in geological formations or used for other purposes, such as creating synthetic fuels or other products. The overall goal of DAC is to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere cost-effectively and sustainably.
One of the main advantages of Direct Air Capture is its ability to capture carbon dioxide from the air regardless of its source. This means that DAC can remove CO2 emissions from a wide range of activities, including industrial processes, transportation, and other sources. This makes DAC a versatile tool for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change on a global scale. Additionally, DAC can be deployed in a variety of locations, making it a flexible solution that can be implemented in different regions based on their specific needs and resources.
Another key benefit of Direct Air Capture is its potential to complement other carbon reduction strategies. While efforts to reduce emissions at their source are crucial for addressing climate change, DAC offers a way to remove CO2 that has already been released into the atmosphere. This can help offset emissions that are difficult to eliminate through other means, such as those from existing infrastructure or industrial processes. By combining DAC with other mitigation strategies, countries and industries can work towards achieving their emissions reduction goals more effectively.
Despite its promise, Direct Air Capture is still a relatively new technology that is in the early stages of development and deployment. As a result, some challenges need to be addressed to scale up DAC and make it a more widespread solution for combating climate change. One of the main challenges is the cost of DAC, which can be expensive compared to other carbon reduction methods. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on finding ways to reduce the cost of DAC and make it more economically viable in the long term.
Another challenge facing Direct Air Capture is the energy required to operate the technology. Capturing carbon dioxide from the air requires significant energy inputs, which can make DAC less efficient and potentially increase its carbon footprint. To address this issue, researchers are exploring ways to power DAC facilities using renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power. By using clean energy to operate DAC, the overall environmental impact of the technology can be minimized.
Overall, Direct Air Capture holds great promise as an innovative solution to combatting climate change. By capturing carbon dioxide directly from the air and storing it in a secure location, DAC offers a way to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and help mitigate the impacts of global warming. While there are challenges that need to be overcome to scale up DAC and make it a more cost-effective and efficient technology, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these issues. With continued innovation and investment, Direct Air Capture has the potential to play a significant role in the transition to a more sustainable and low-carbon future.
